3D scale model making is skillful craftsmanship.
Architectural model making is an indispensable design tool for architecture students and architectural designer.
In fact, at present, architectural model making is not just a leisure activity that brings 3d scale model making hobbyists a fun and rewarding experience, it is also professional workmanship.
A convincing architectural model may comprehensively capture the excitement and essence of the designer’s vision.
On the contrary, an undesirable scale model may become a failing representation in presenting and communicating design ideas.
This guide has a wealth of valuable and practical architectural model making and fabrication tips.
This general advice may assist you in improving model making skills and avoiding common mistakes made by a newbie.
Each chapter looks at one or a few principal areas of architectural model making process.

CHAPTER 1:
Tips of Before Making Architectural Model
The architectural model is seen as a bridge between a design idea and its realization.
When making architectural models, everyone has their own tricks and habits.
Learn from the previous model making experience and learn from others’ strong points are the key to success.

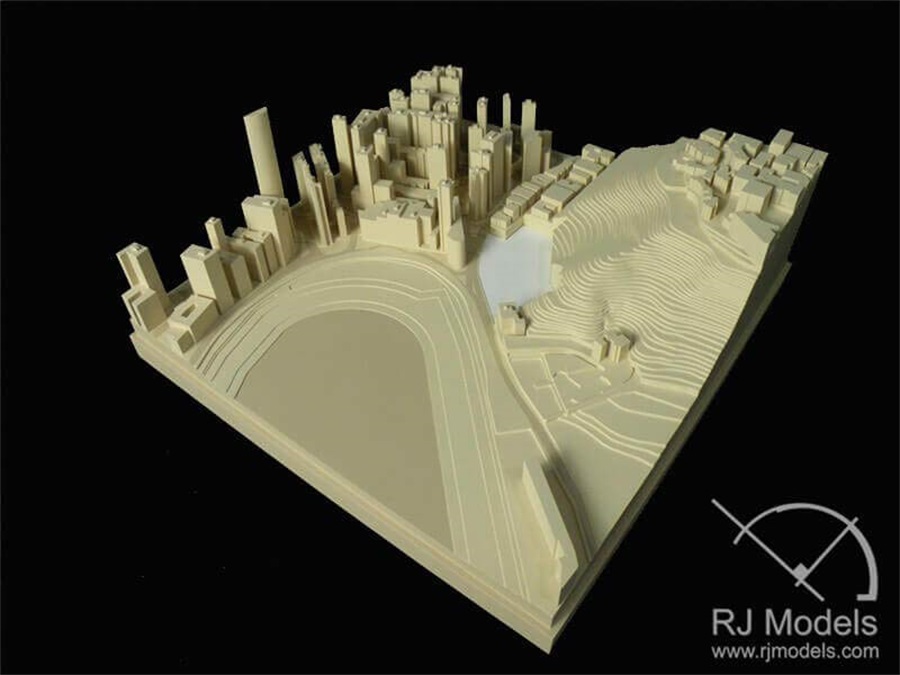
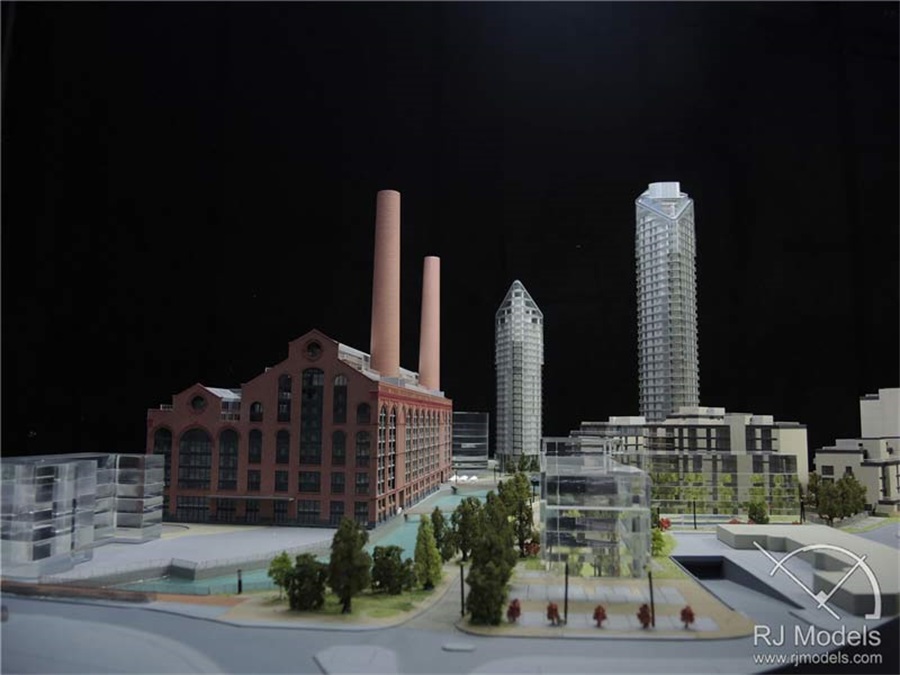
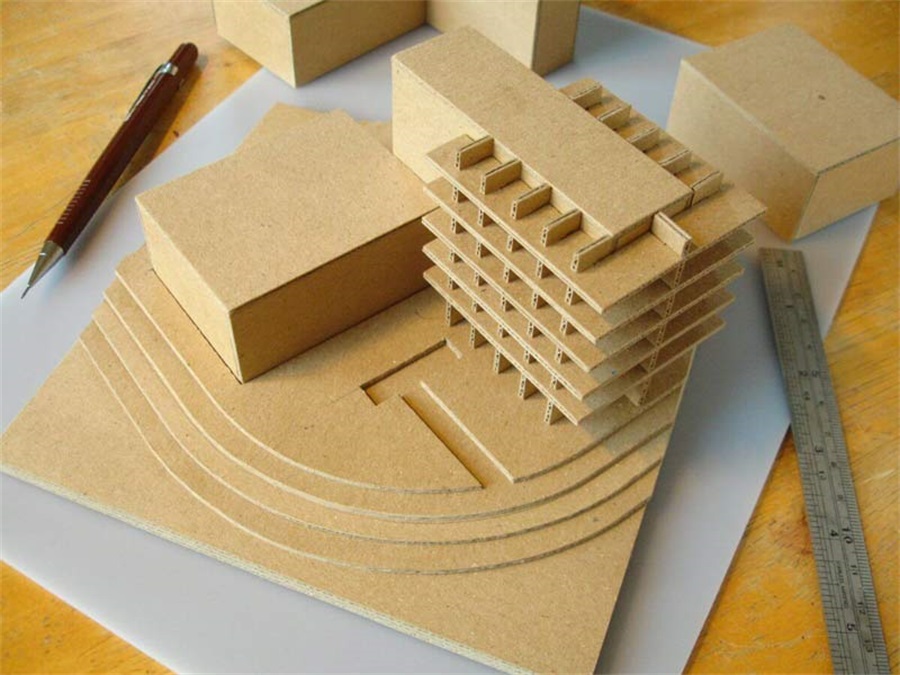
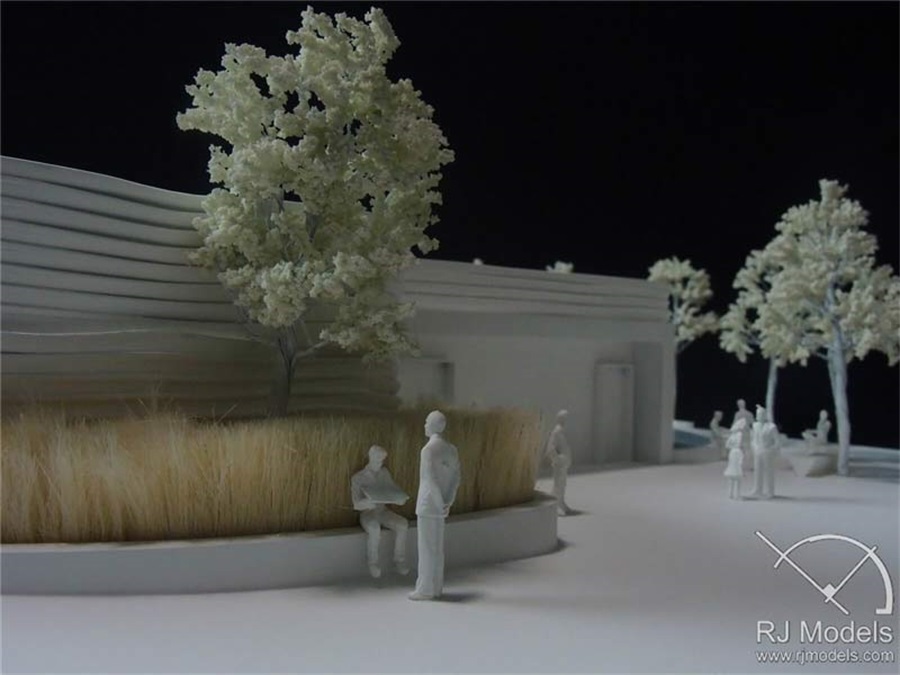
Architectural Model Making Project, Museum of the Future
On the basis of the rich experience of architectural model making, project presentation and exhibition, Chapter 1 provides a series of general model making suggestions which are more about ways of thinking.
This chapter does not go into specific details of architectural model making techniques and materials.
Instead, the following are some basic rules that will save you some of the wasted time, cost and effort.
C1.1: Tip 1. Always Start by Thinking
Before commencing the architectural model making process, it is crucial to define the intent of the architectural model.
In other words, determine the purpose of making the model before constructing.
Architectural models serve various functions.
This mainly depends on the types of architectural models.
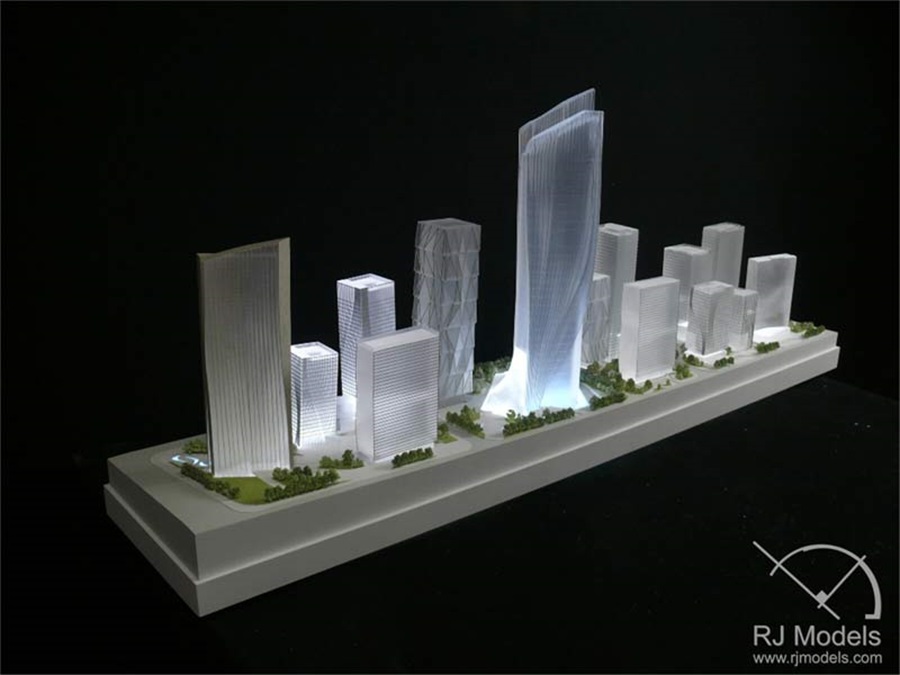
The conceptual architectural model may assist in exploring initial design ideas.
These models are relatively simple and easy to adjust as the design is progressed.

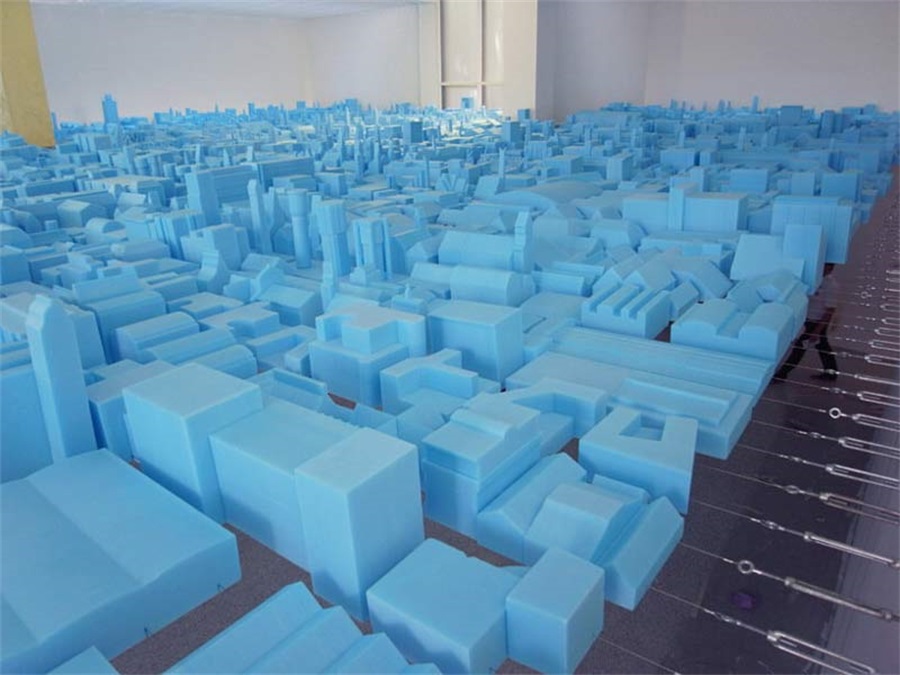
Architectural Model Making Project in Tokyo, Shibuya
Working architectural models may be required to demonstrate specification in architectural design, such as detailed building forms and materials.
Served as ideal communication tools, working models are usually made of higher quality materials and include more design detail.
Conceptual Model Making Project in China
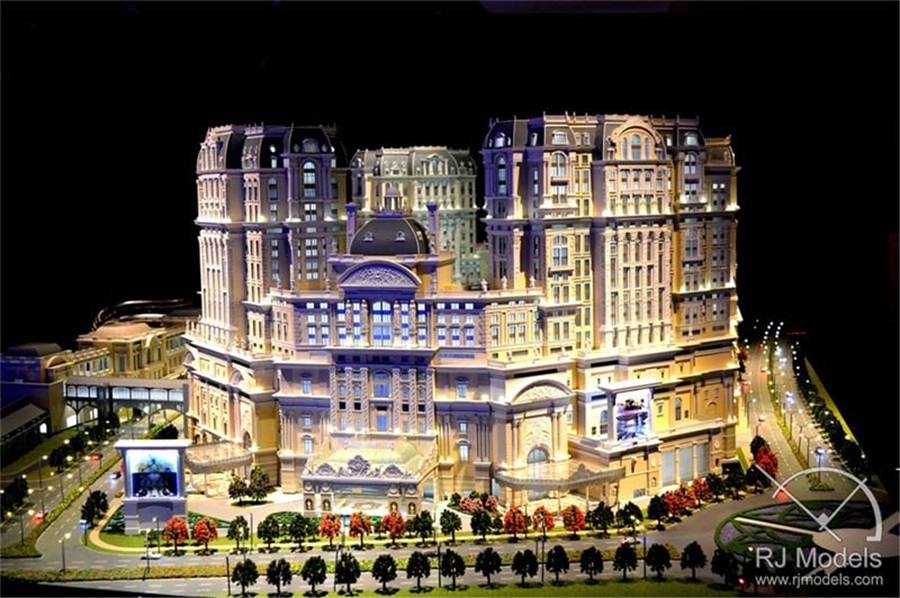
Presentation architectural models are wildly used to help designers and clients, sometimes the public, to envisage the projects.
Also, presentation models are considered as ideal marketing tools for developers to attract potential purchaser and investors.
Therefore, these models are far more detailed with impressive displaying effects.
Think over what you want to represent and achieve, and what you expect the viewers to see and understand by looking at your architectural model.
C1.2: Tip 2. Make a detailed architectural model making plan
Completing an architectural model always take longer than you planned.
Very often it is one with skillful handicraft do not finish their architectural model on time.
That is mainly because they wanted to show too much and have spent lots of time on some specific parts.
And other architectural model elements have to be rushed or haven’t got done at all.
Generally, if you want to incorporate more details in your architectural model, more time and effort you have to spend.
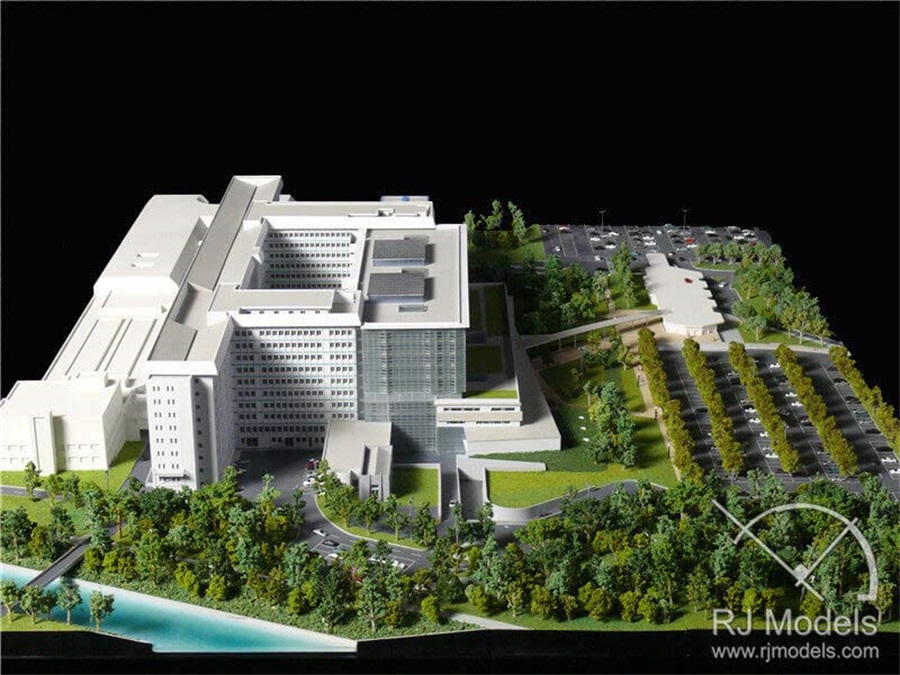

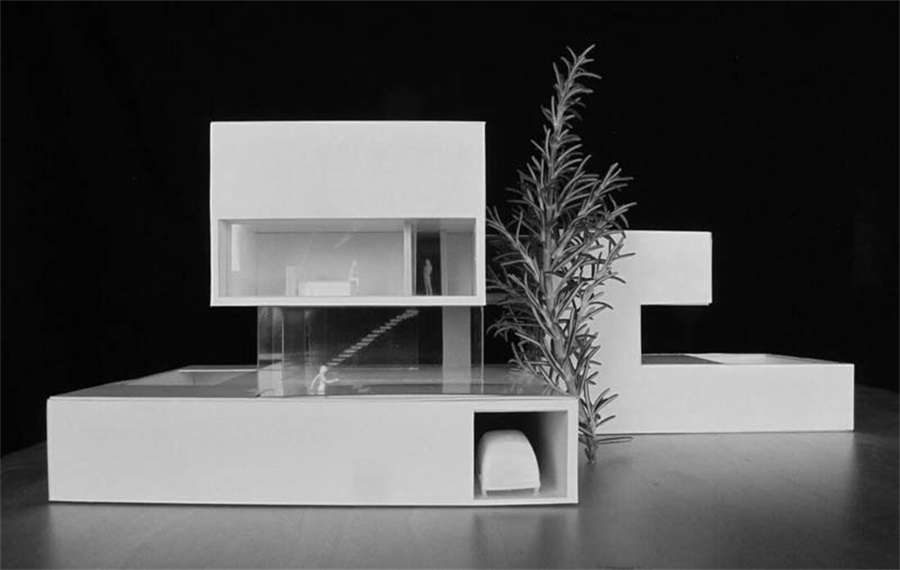
Presentation Architectural Model Making Project in France
If the time is limited and urgent, do not try to present all the detail of your design.
Think comprehensively about the architectural model making time, material and tools available to you.
Just like every construction project needs a comprehensive construction scheme and working schedule,you‘d better make a detailed plan regarding material and size of the model components, as well as the model making order.
Try to be realistic and looking for the balance to optimally realized overall architectural project presentation.
C1.3: Tip 3. Determine the Appropriate Architectural Model Scale
The scale is one of the predominant factors to fabricate a successful 3d architectural model.
Architectural model scale mostly depends on what you plan to showcase, and how big an area you need to model.
The smaller the scale, the more difficult it is to depict the project’s details accurately.
For example, 1:25 scale is ideal for an interior architectural model making.
With this scale, the viewers are able to see the detailed components of the room.
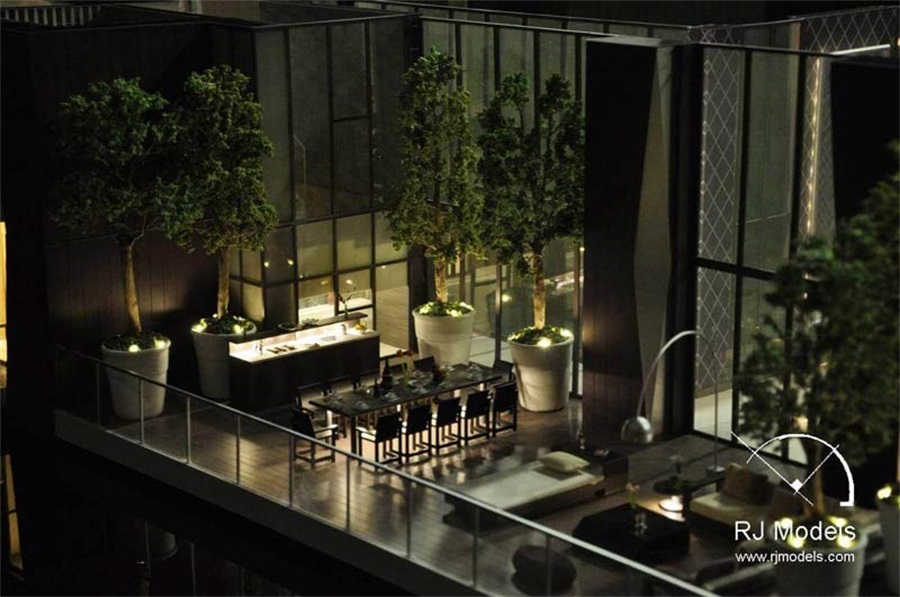

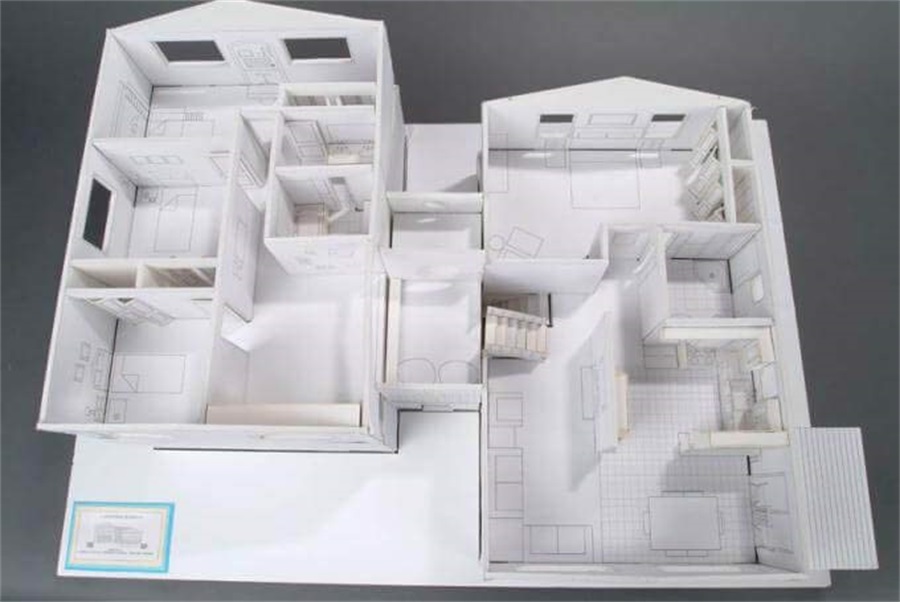
Interior Model Making Project in India, Mumbai
Even the soft furniture such as armchairs, sofas can be seen from an exquisite interior architectural model.
Understanding architectural models scale clearly will enable you to work out which route to go down for your particular project.
It is important to decide what scale that your architectural model would be best suited to.
Having good thinking about the scale after considering what you want to illustrate, the architectural model making time and budget, and material and techniques available.
C1.4: Tip 4. Be Selective About the Detail
Attention to detail is a must in architectural model making process.
Nevertheless, it is highly unlikely to complete an architectural model with all the details that you want to convey in your project presentation.
Mainly because of the time and budget you have do not allow you to do so.
Figure out what you want to highlight in your architectural model instead of making an exact replica of the design.
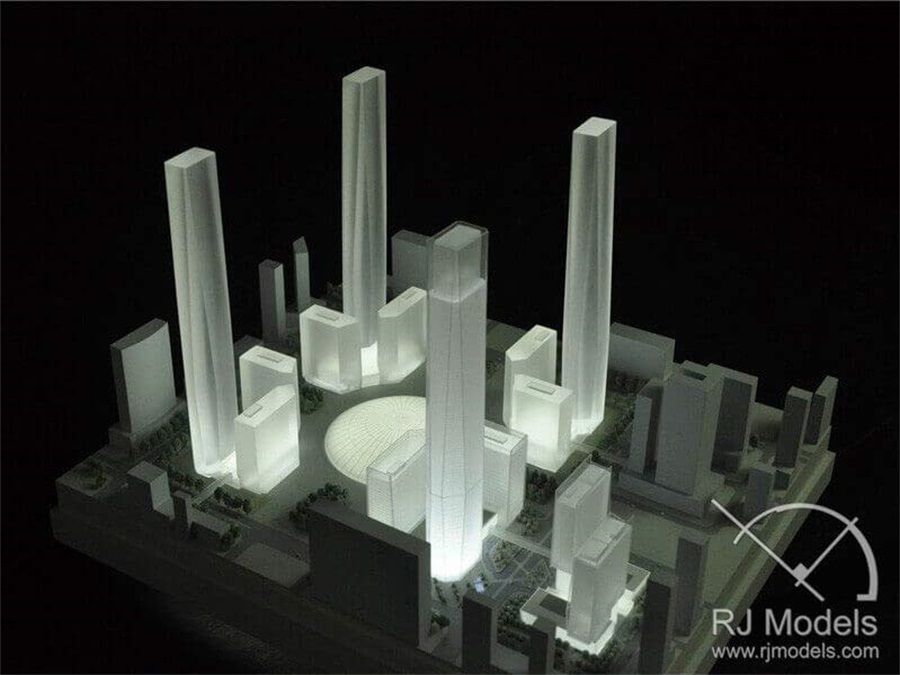

A Monochrome Massing Model Project in China
For example, you want to showcase a new proposed building in a sensitive area.
In this case, a monochrome massing architectural model will be an ideal choice.
The recommendation here illustrates the surroundings using blocks with basic forms and similar-looking materials.
Therefore, the viewers will be able to get an instant and straightforward understanding of your architectural design project.
Remember it is not always necessary to produce the entire structure and context.
Sometimes a well-selected section through the building can bring unexpected effects.
C1.5: Tip 5. Pay attention to design drawings.
Architectural plan drawings are commonly used as the base of the architectural model to ease the model making procedure.
Print architectural plans and have some copies, in case the used one being destroyed by accident.
Other architectural drawings and digital models are equally important as they are the ‘foundation’ of your architectural model.
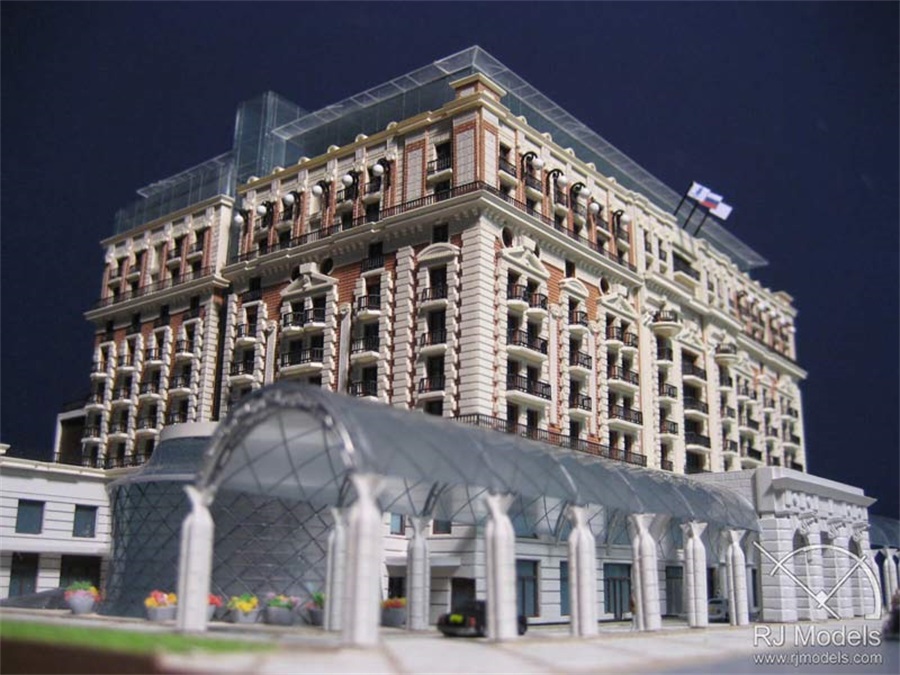
Architectural Model Drawing for Hotel Model in Macao
Ensure you are familiar with the design and modeling software and have sufficient knowledge of architecture.
This helps you to transit abstract architectural design ideas into dramatic physical exhibits.
It’s better if you can ensure the model making drawings you are using is the final design. In most cases, the occasional design changes may affect the model making progress. And therefore influence the quality of the architectural model.
If the change of the design is significant,for example, the building structure has been modified,you having to rebuild the related parts of the model. And yes, the model making progress and quality will be affected.
C1.6: Tip 6. Make an ideal working space for yourself
Architectural model making process may easily get messy and confusing very quickly if you do not have enough working space.

Make sure you have a well-organized and spacious working environment.
One recommendation is setting up different working areas.
For instance, having architectural model cutting area separated from assembling and post-processing area.
This will bring you a pleasant model making experience and will prevent you from wasting time and efforts.
In addition, having a good lighting condition is important as well.
In most cases, you need to cut model architectural model making with scalpels and craft knife very often.
And it will be better if you have several luminous lights passes.
It will help you to get a cleaner cut and you will be less likely to hurt your fingers.
C1.7: Tip 7. Get organized
The organization of architectural model making components, no matter unfinished, completed or purchased, is necessary.
In particular, when the architectural model you plan to make has a huge size but need to be highly detailed.

Arranged every piece in order is a useful trick.
You will have hundreds of model components to assemble in the later architectural model making a stage.
C1. 8:Tip 8. Wash your hands from time to time
Architectural modeling specialists suggested that washing hands every 1 hour is a good model making a habit.

Wash your hands frequently may prevent you from being insanely frustrating once you find your left fingerprints or spots on the models. (Image from internet)
Especially, when you are working with white and clean architectural model making materials.
Dirt, oil, and glue on your fingers will smudge your 3d scale model.
1.9:Tip9. Show the tangibility and intimacy of the architectural model
In general, architectural drawings are lack of tangibility and intimacy that physical architectural model has.
Make sure the architectural model you build can provide the viewers with a deep understanding and help to increase spatial awareness.
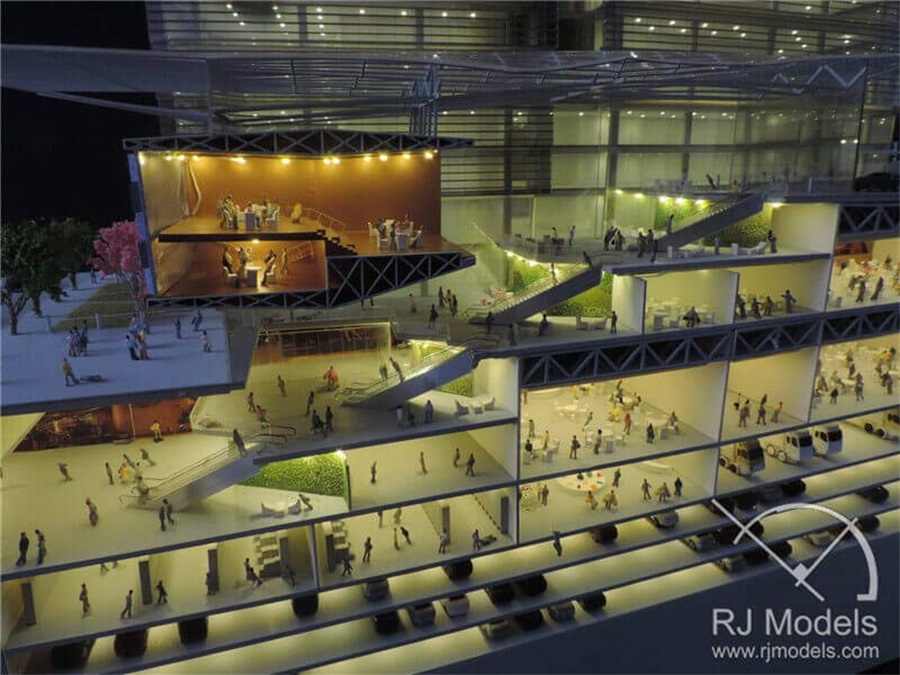

Choose the right methods, such as add special lighting effects and lifting functions will enable you to achieve the best architectural model displaying effect.
C1.10: Tip 10. Stop, check and ask for advice
Sometimes, you may easily go too far into making unnecessary and superfluous detail, or the completed components are over-structured.
Think over the big picture before you moving on to the next model making stage.
Take a look at your underway 3d scale model from all angles.
And stop to check back and forth between your architectural model and original blueprints.
In addition, do not hesitate to ask for advice and help, whether from 3d scale model makers, colleagues or friends.

Listen to their suggestions and criticisms and you may generate alternate ideas and creative views.
Should you have any query of the architectural model making, we also have many 3d scale model making experts, who are willing to answer you, welcome to send the email to us: marketing@rjmodels.com.hk
CHAPTER 2:
Tips for Choosing the Architectural Model Making Material
The architectural scale model is supposed to be more informative than the design itself in illustrating the central design ideas and intentions.
In the past, architectural scale models were mostly made out of paper, foam, wood, and clay.
At present, the 3d architectural scale model markets provide a wide range of material options to enrich the display effects of architectural model making.

High-quality architectural model material can be made a high-quality miniature building model
Combining with practical architectural model making the experience, Chapter 2 encompasses a series of tips that help you to choose the right model making materials.
These architectural model making tips can go quite well beyond for the architectural students and model making hobbyist.
And it may bring your architectural model making skills to be more professional.
C2.1: Choose the Most Appropriate Materials
Select the right architectural model making the material can assist you to complete a satisfyingly impressive and convincing architectural model.
Architectural model material selection depends on various factors.
In general, architectural presentation models are mostly made of stable and durable architectural model making materials.
They need to be robust and the color of the model won’t fade easily.
That’s because these kinds of models will be exhibited for a related long time, and will be exposed to sunlight and dust.

Nowadays, people prefer to the durable and high-quality model making the material.
It will be better if the architectural model making the material you chose is easy to work with.
Besides, consider your model making budget and time limits is necessary as well.
The basic rule of choosing the right architectural model making material is to have a clear idea of what you want to present.
You can choose 2 – 3 types of modeling materials for model making, but do not use too many kinds of architectural model making materials or your model will look tacky and unconvincing.
The following are some basic references for anyone who wants to know how some frequently-used model making materials dictate the design.
C2.2: Plastic
C2.2.1: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS is one of the commonly-used modeling materials that lots of professional architectural model making firms utilized.
It is strong and lightweight, but kind of expensive.
You can paint the finished ABS products with a broad range of colors.
Generally, during the architectural model making process, ABS often is cut using by a laser cutting machine.
It is efficient and the outputs can be held over 10 years.
Because of its high-resolution character, and somewhat flexible, ABS is wildly used to making presentation architectural models.

Architectural hotel model made of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
C2.2.2: Acrylic Board and Perspex
Acrylic board for architectural model making comes in multiple thicknesses.
Its hardness and easy to machining feature make it easy to handle and cut.
However, it is expensive and needs certain architectural model making equipment to manipulate.
The architectural models made out of acrylic board or Perspex is quite stunning.
You can express your designs actually by providing the viewers amazing visual experience.

Architectural model made of Acrylic Board
Because of the nature of this architectural model making material, glue marks can be apparent around cutting lines and edges.
Transparent and translucent acrylic boards are often used to producing architectural model windows and building facades.
Keep in mind it is kind of complicated to make curved shapes as the acrylic board needs to be polished, repeatedly.
Perspex is getting more and more popular in the architectural model making area recently.
It is similar to transparent acrylic but has a better effect.
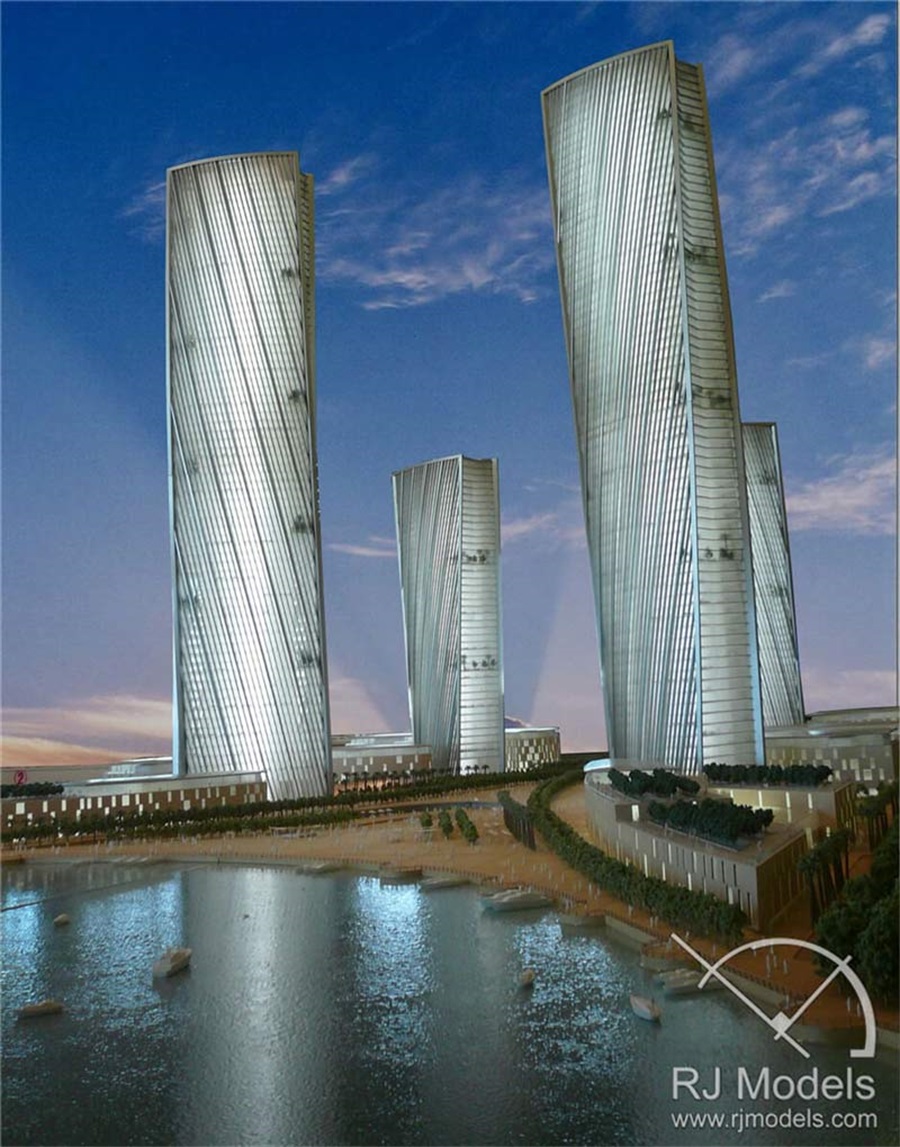

And it has a perfect effect once you use it to make the water surface and match up with lighting.
You are able to find Perspex with different sizes and color, either transparent or semi-opaque, in most architectural model making craft stores.
Lots of 3d scales model makers use Perspex to build architectural model buildings.
C2.2.3: PVC board
Architectural model made by PVC board
PVC board is the most frequently used architectural model making materials in making main structures of the buildings.
It is cheap and easy to work with, and you can complete a PVC architectural model very quickly.
Considering the PVC board has a limited choice of colors, it is more used for conceptual architectural model making.
Sometimes they are used to constructing terrains or model bases.
C2.3: Wood
C2.3.1 Wood and Balsa wood
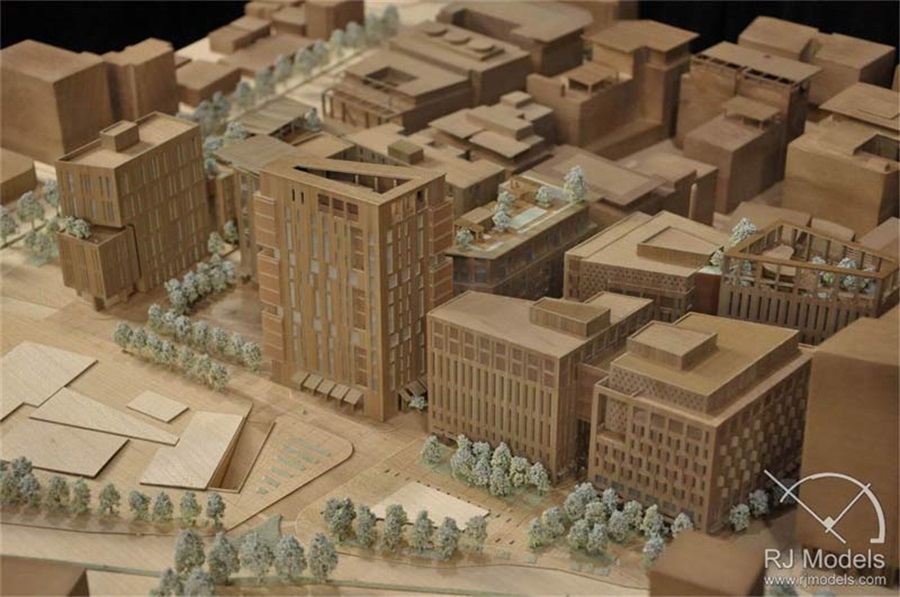

Architectural model made by wood
Just like cardboard and foam board, balsa board is an easy cutting and painting architectural model making material.
It can be used to create accurate architectural models.
Balsa wood has a fine finish and is available in various weights.
Most architectural model making hobby and DIY shops sell Balsa wood both in thin sheets and in sections.
Nonetheless, it is kind of expensive.
Balsa wood is one of the best materials to produce highly detailed structural architectural models.
Also, the balsa wood board is often used to make the pedestal for heavy architectural models.
And lots of timber constructions are made out of balsa strips to form the wooden trusses and building skeletons.
It is now the most popular wood product for architectural model making.
C2.3.2 Cork Sheets
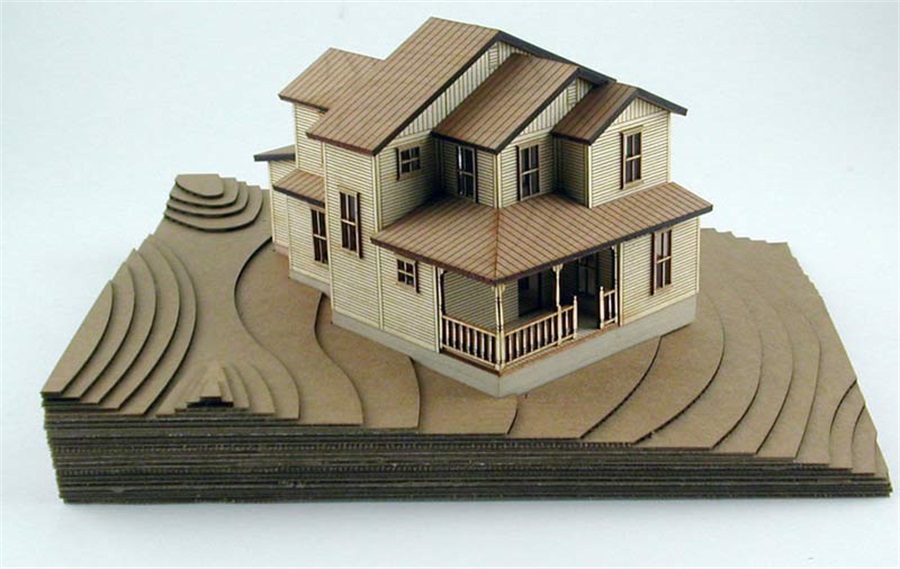

Architectural model made by cork sheets
Cork sheet used for architectural model making has a very natural finish.
It is flexible but kind of breakable.
Therefore, it is not easy to cut, especially if you cut it parallel to the grain.
In your architectural model making cutting stage, raw edges appear very often once you cut it along vertical texture, and you need to rub them with sandpaper.
It is ideal for modeling hilly sites of architectural models once you build a group of cork sheets up in layers.
C2.4: Paper
C2.4.1 Card and Cardboard
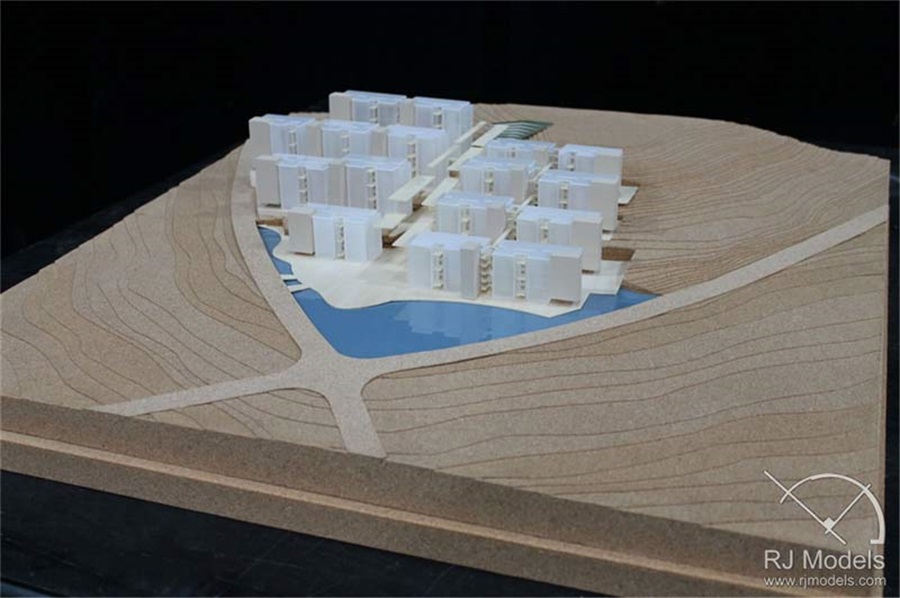

Architectural model made by cardboard (Image from internet)
Cardboard is an architectural model making material to make the task of the landscape.
It is easy for building conceptual and working architectural models.
Cardboard is cheap and has a versatile color, weight, and thickness and finish choice.
This architectural model making material is commonly used to produce architectural model roads and paths.
Terrains can be easily represented by building up layer upon layer of cardboard.
Grey cardboard is suitable to represent fair-faced concrete for its natural texture.
C2.4.2 Paper and Kraft paper

Massing model can be made by Kraft paper(Image from internet)
Kraft paper is a cheap and robust architectural model making the material.
It is very easy to find and manipulate.
It can be used to present most buildings and structures, including some lake surface or some other special model sites.
C2.5: Foam

Foam and polystyrene are a basic architectural model making materials. (Image from internet)
They are relatively light in weight, thus easy to transport.
Foam is the most frequently used one as it is easy to cut and you can buy it at any craft shops.
It is an ideal architectural model making material to create conceptual architectural models as it is easy to cut and shaped.
But it is relatively fragile and easy to be damaged.
That’s why foam is more used to making conceptual models instead of presentation architectural models.
C2.5.1 Insulation Board

Interior model made of insulation board (Image from internet)
Insulation board is a light weight architectural model making material and easy to model with.
The drawback is it is not very strong and easy to be damaged.
It always crumbles on the architectural model edges.
You are able to build small-scale buildings using insulation board, but not in every detail, in a very short time.
The more common use of this architectural model making material is to build building walls of the interior architectural model.
C2.5.2 White Foamboard

Villa model made of white foam(Image from internet)
White Foamboard used for architectural model making has a variety of thickness.
3mm and 5mm whiteboard are the two most common types.
It has a lightweight property and is built strong and not very to dent and crush.
This kind of architectural model making material is often used for constructing architectural model bases and building walls.
C2.5.3 Foam sheets
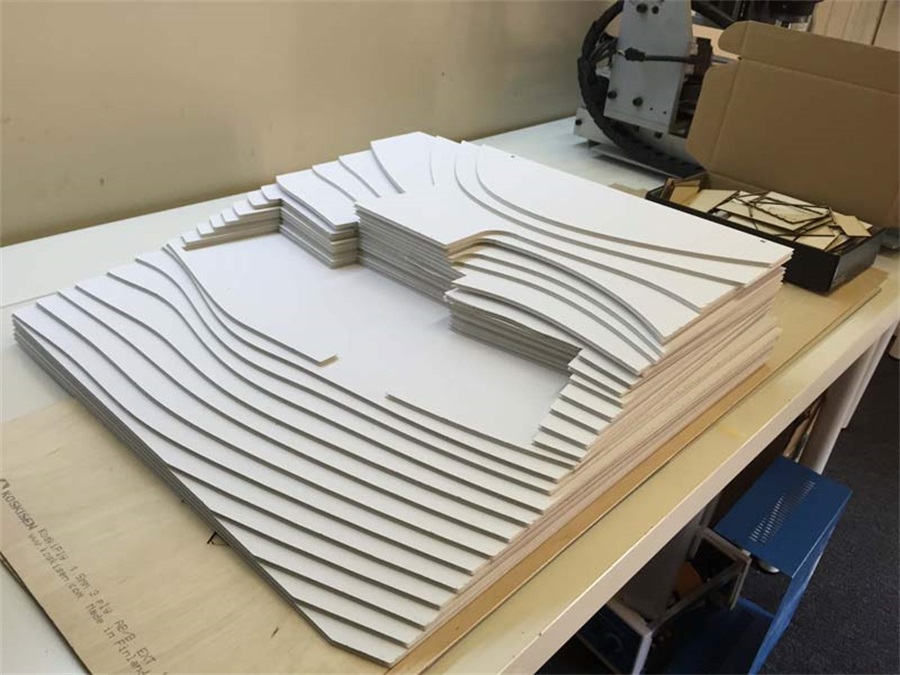
Landscape model made of foam sheet (Image from internet)
Foam sheet comes in a wide range of weights, colors, and thicknesses.
It is weighted light but pretty sturdy. Foam sheet can be simply cut with scissors.
This basic architectural model making material is very useful for making massing architectural models or topography, especially producing clean white context architectural model.
It is ideal for creating neat junctions and corners as well.
C2.6: MDF
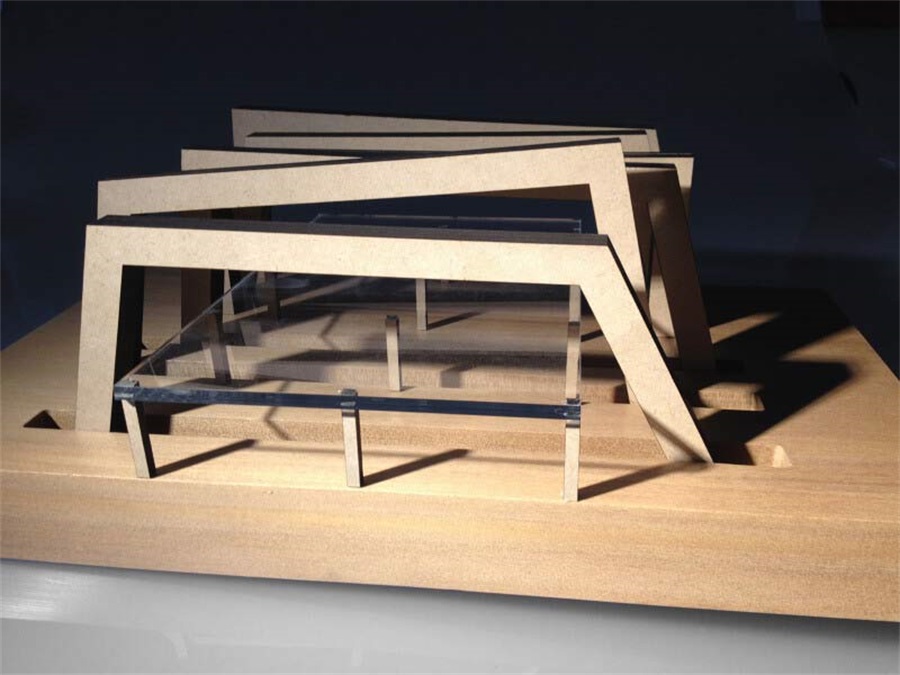

Thicker MDF is useful for making rigid architectural model bases.
MDF is an architectural model making a material with a good finish and needs no sanding.
But is expensive and requires advanced architectural model manufacturing equipment, and you need to inspect for cutting and shaping it.
During the architectural model making process, MDF is often used to produce large architectural models of buildings, in particular, when you want to showcase the interior layout.
C2.7 Metal
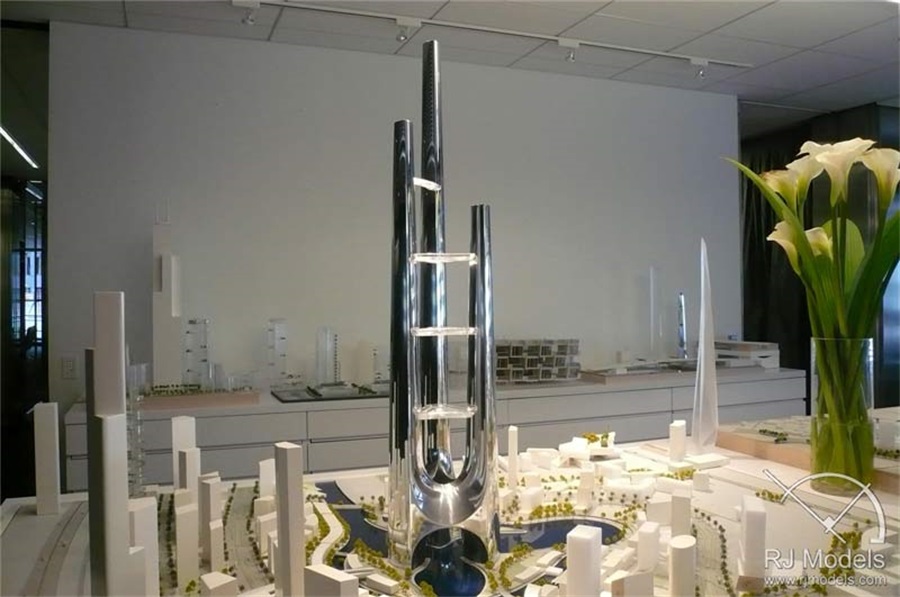

City Planning Model made of Metal (Image from internet)
Metal is one kind of high standard architectural model making material, which needs model making machines to deal with.
It is expensive but has amazing displaying effects.
As metal has a varied choice of color and texture, it is often used to demonstrate architectural model building finishes.
The frequently-used metal sheet for architectural model making, including aluminum, brass, steel and copper sheets.
C2.8 Clay and Plasticine
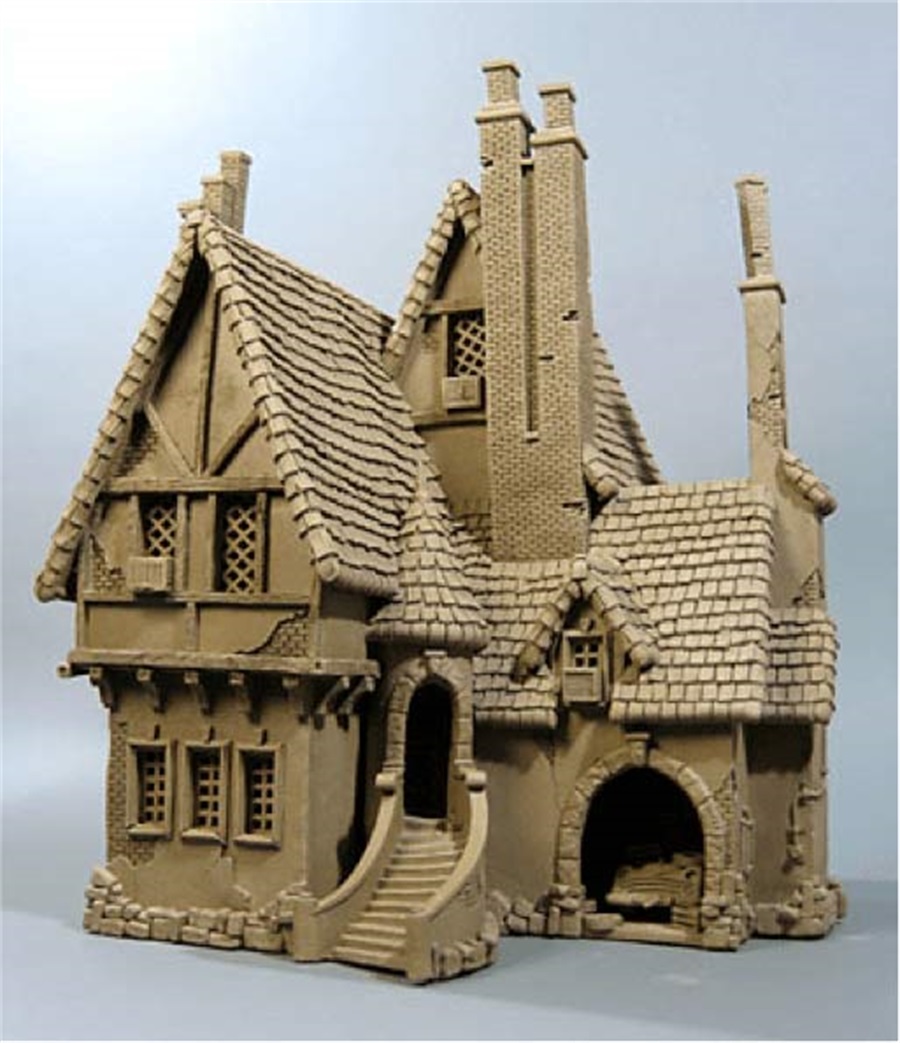

Model made of Clay (Image from internet)
Clay is probably one of the cheapest architectural models making the material by far.
It is soft, smooth, and rubbery and can be used to create any shapes.
But it is not ideal to produce a very fine and sharp shaped architectural model.
Plasticine has better properties as it can remain workable even after exposure to the air for a long time.
However, it means that architectural models made out of this architectural model making material are not durable.
As it will shrink and crack with time, it is more used for making conceptual or working architectural models.
Also, clay and Plasticine are particularly useful for creating hills or steeply sloping and unique building shapes.
C2.9: Buying some premade architectural model making materials
Using premade architectural model making materials can be the finishing touch that helps you to elevate the architectural model to a more professional level.
The online shop provides a wide range of premade model people, cars, street furniture and lighting, miniature figures and plants, etc.
You can also find them from the local Art & Craft shops.
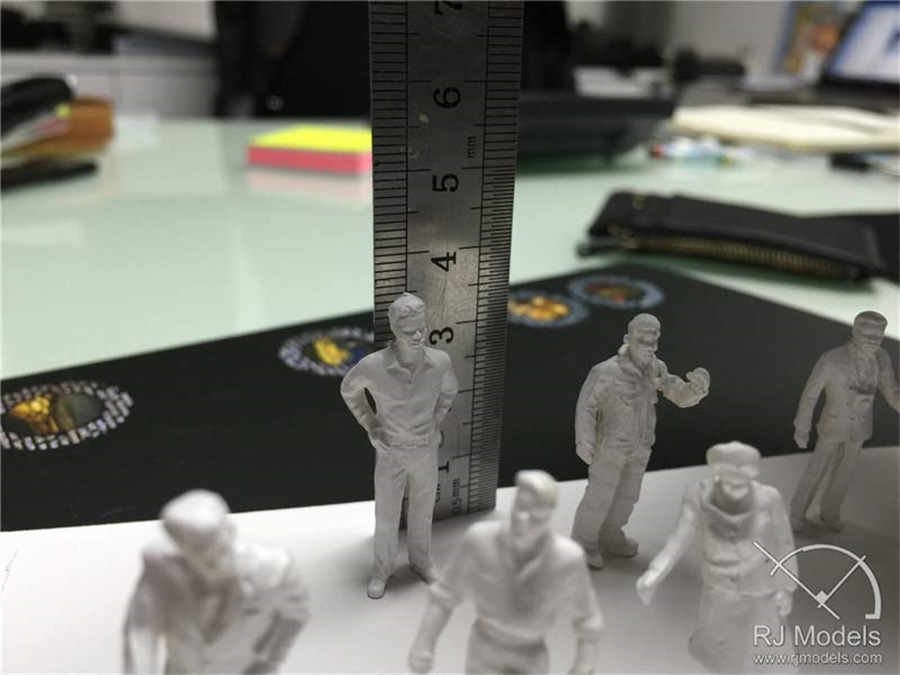

Model people
Under most circumstances, you can use bags of course turf or flocking to create a grass cover effect.
Adding some landscaping elements in the later architectural model making stages, such as model plants and trees allows your architectural model to look more vivid and natural.
The key point here is choosing the objects that conform to the architectural model scale that you used.
Otherwise, the completed architectural model will look distorted and absurd.
C2.10: Figure out where to get them
After you basically decide what architectural model making materials to use for your 3d scale model, you need to think about how to get them.
Some architectural model components, such as model figures and trees, are not easy to shaped or modeled, or you have a relatively tight schedule.

Example of premade architectural model making materials, trees, people, etc.
You can approach them from an architectural model making Art & Craft shops, or make an order online.
Also, online shops such as Amazon and eBay, or dedicated websites like 4D Model Making Materials (see useful links below), provide you with more options.
These models making supplies websites have an abundant on-line catalog that assists you sourcing your required architectural model making material.
Moreover, you can always find unique items you couldn’t find in model stores, or purchase the objects you want with an affordable price.
Just Google ‘architectural model making materials’ and you will find plenty of choices.
https://www.ebay.com/sch/i.html?_nkw=model+building+materials&ul_noapp=true
https://www.amazon.com/slp/model-making/x9fwj7s56kqa3pa
C2.11: Deal with the architectural model making material properly
Of course, the most important thing to complete an excellent model is to cut, shape and assemble your model making a material with accuracy and circumspection.
One trick here is using different textures or thickness of the same architectural model making material to achieve rich display effects.
Using the correct thickness can give your architectural model a much better sense of accuracy, as your model will have a satisfyingly high level of precision.
Try to be creative and make full use of reclaimed and leftover architectural model making materials, including unconventional architectural model making materials like fiber.
Remember to make sure all the architectural model making material you selected are sturdy enough. Otherwise, your hard work will be wasted.
Last but not least, make sure all the architectural model making the material you used for the completed product looks “comfortable” and “harmonious”.
CHAPTER 3:
Tools for Architectural Model Making
Before the construction of any architectural model, you must first ensure you have all the necessary tools.
Architectural model making requires the use of many different tools.
It is essential to choose higher-quality tools that are specifically suited for this type of modeling.
A high-quality model making tool is not only more durable but it also dramatically improves the efficiency of the process and provides the model maker with better building experience.
The tools mentioned in this article can all be used to complete most model making tasks.
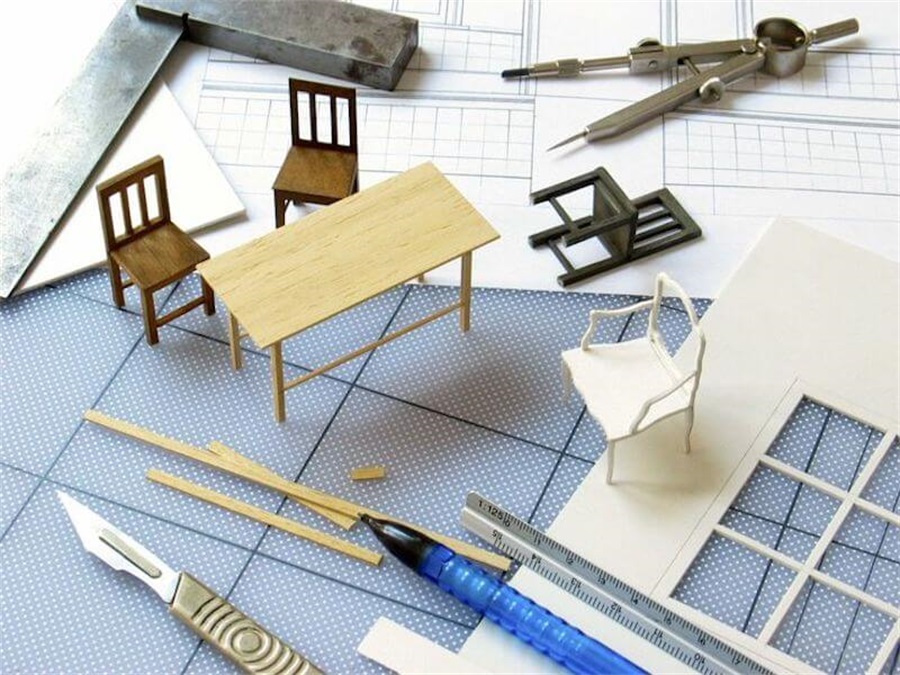

Tools for Architectural Model Making
Combining with practical architectural model making the experience, Chapter 3 encompasses a series of tips that help you to choose the right model making materials.
These architectural model making tips can go quite well beyond for the architectural students and model making hobbyist.
And it may bring your architectural model making skills be more professional.
C3.1 Cutting Tools
There are many different types of cutting tools available for different uses that are made of varying materials.
There are even professional cutting tools available for the construction industry.
In this article, we will elaborate on a few of the most commonly used cutting tools in architectural model making, and you can choose which ones you are accustomed to using.
C3.1.1 Cutter
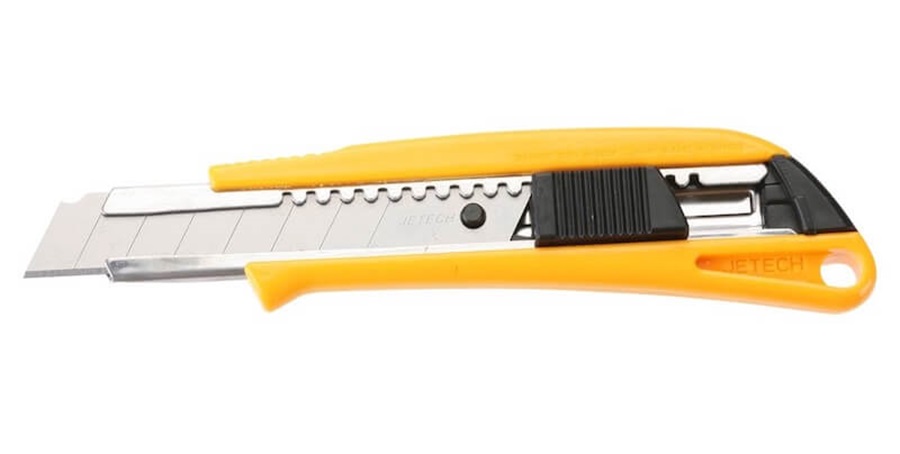

A Cutter comes in 60° angle
A cutter is a most frequently used tool in architectural model making, so we need to familiarize ourselves with the makeup of a cutter, as well as know the different components and their uses. We must also learn the techniques required to use the cutter safely.
1. The blade of a cutter is scored with slanted lines.
When the blade becomes blunt, you can snap off the blunt section of the knife blade along the scoreline to reveal a brand new cutting blade, making it very convenient when it comes to replacing the blunt part of the cutter.
2. A commercially available small cutter has blades that come in a 30° and 60° (58°) angle.
When making an architectural model, many details require precise handling, and a 30° angle blade is most suited for such precision cutting.
We highly recommend that you purchase one.
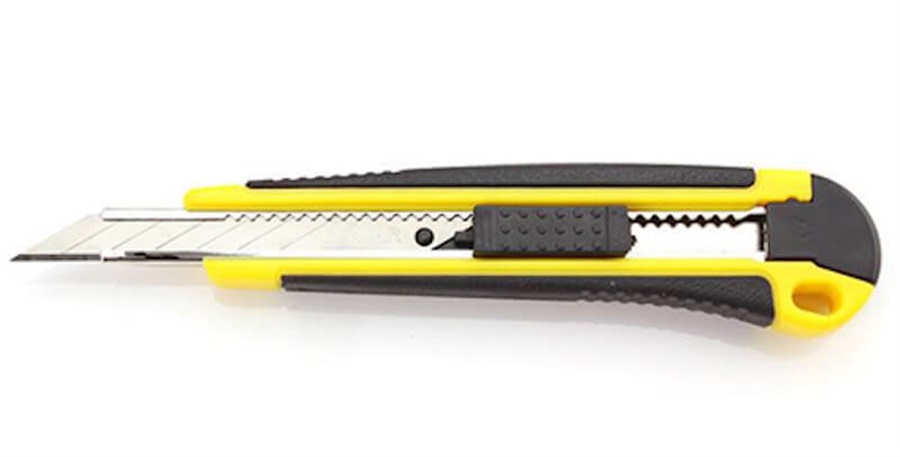

A Cutter comes in 30° angle
3. The trick to cutting board of material with a cutter is to avoid trying to cut it in one motion, as this will use too much force, resulting in an uneven cut.
To ensure a high-quality cut, use between 30%-40% of strength and repeat the cutting motion on the same line 3 to 4 times to cut through the board of material.
4. The cutting motion must be quick and without hesitation.
Do not go too slow as this will result in an uneven edge.
5. The blade of the cutter must not stretch too far out of its casing. It is sufficient to extend the knife blade by 1 or 2 snap-off sections.
When the knife blade extends too far out, it becomes unsafe as the blade can bend and potentially break under pressure.
Moreover, the cutting motion with a blade that extends too far out will be less steady, rendering it impossible to produce a neat and smooth line.
6. Using a cutter with a very blunt edge can cause one of the most common injuries during the architectural model making.
As the knife edge is not sharp, we naturally use more force and this force increases the risk of the knife slipping and cutting your fingers.
Hence, always replace the knife blade once it is blunt.
7. For safety reason, always snap-off the blunt section of a blade with pliers or similar tool to prevent the snap-off segment from scattering off, resulting in injuries.
8. For convenience, store all the blunt knife sections in a temporary container and dispose of this correctly afterward. An old tin can will suffice.
Although the blade snapper is designed to break off the blunt section of the blade, the broken-off piece can still bounce off easily.
The blade holder of this tool can also deform as a result of frequent use, so it is best to avoid using the built-in blade snapper.
9. Some cutters come with a built-in blade snapper generally at the top.
The blade snapper has a slot to hold the knife blade in place.
10. Lastly, always store the cutter in a dark and dry place to prevent rusting.
C3.1.2 Acrylic Cutting Tool

Acrylic Cutting Tool
Cutting a plastic board is less complicated.
During cutting acrylic board, please cut with a firm downward motion.
Repeat this action a few times before breaking off the sections of the board.
C3.1.3 Model Making Scissors

Model Making Scissors
Scissors are mainly used for paper and general cutting.
There are also metal multifunctional scissors for cutting metal sheets.
1. Some may think that a cutter is sufficient for cutting paper, but a pair of scissors is better when it comes to cutting a large piece of paper.
2. Ensure you buy a pair of scissors with a comfortable grip on the handle to prevent injuries following a long period of use.
C3.1.4 Modeling pliers

Modeling pliers
1. We use combination pliers or diagonal pliers to cut steel or copper wire.
Compared to a standard pair of scissors, the pliers are more useful for cutting steel and copper wire.
Diagonal pliers are used explicitly for snipping wire while combination pliers are used for cutting off the wire or bending metal material.
2. Another type is needle-nose pliers that can be used for bending and twisting wire.
In architectural model making, the work often involves a lot of tiny details.
Hence, having needle nose pliers will prove very useful when handling such details.
C3.2: Measuring Tools
In addition to being used for correct measurements, the measuring tool is used for line drawing and as a cutting guide.
C3.2.1: Ruler

Rulers
1. A ruler is often used as a cutting guide with the cutter, so its composite material must be durable and not easily chipped or cut by the knife blade.
The most suitable ruler is those made of stainless steel or aluminum alloy.
2. It is especially true for a stainless steel ruler, which is slightly weighted. When held down firmly with your fingers while cutting, the ruler will not move, making it a steadier cutting guide tool.
3. Another feature of a stainless steel ruler is the measurement markings start from the end of the ruler, rather than starting slightly in from the edge, leaving a small unmarked section.
4. Therefore, it is possible during a measurement to align the ruler with the starting point of the object to be measured.
Some rulers have no blanks at either end.
5. Whether you use a 6-inch, 12-inch or 18-inch ruler largely depends on the size of the 3d scale model you are working on.
C3.2.2: Stainless steel triangle ruler, also known as a set square
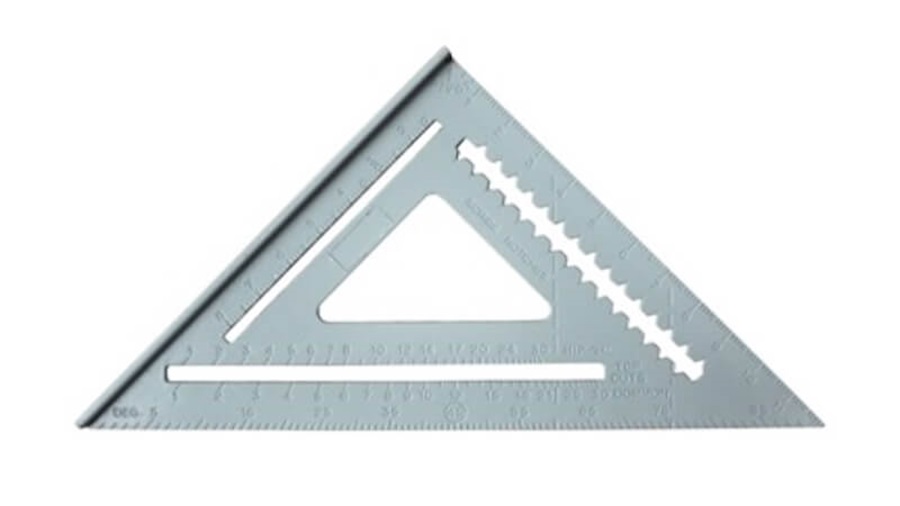
Stainless steel triangle ruler
1. A stainless steel triangle ruler or a set square ruler is used for cutting right-angles.
Most triangle rulers are made of aluminum, but some are plastic triangles lined with a metal edge.
2. When used as a tool to line up and level all components, it allows the maker to assemble the model with accuracy and precision.
3. During the architectural model making, the triangle ruler is mainly used to draw a straight line, parallel lines or as a cutting guide during cutting.
C3.2.3: Wide-based set square (L-shaped ruler)

Wide-based set square (L-shaped ruler)
This is a wide-based engineering square use for cutting right-angle on a piece of board.
Just as for the stainless steel ruler, it is a must-have tool in any cutting work.
Hence, it is essential to grasp the use of this tool well.
The stainless steel L-shaped set square not only measures accurately, but it also allows us to draw and cut a perpendicular line easily.
Some models have an inbuilt spirit level for accuracy.
C3.3 Adhesive Tools
During the architectural model making, we have many different adhesive tools that can be used to bind materials together, and the type of adhesive required depends on the materials used.
C3.3.1: UHU Glue

UHU Glue
This glue is robust, permanent, and bonds well. It dries transparent and is soft when dry.
It is suitable for many kinds of materials, including plastic, wood, paper, and fiber.
It can, however, leave a paste-like mark on the glass. UHU glue is similar to white glue but thicker.
Therefore, it is stronger compared to white glue, and it also dries faster.
C3.3.2: Super Glue
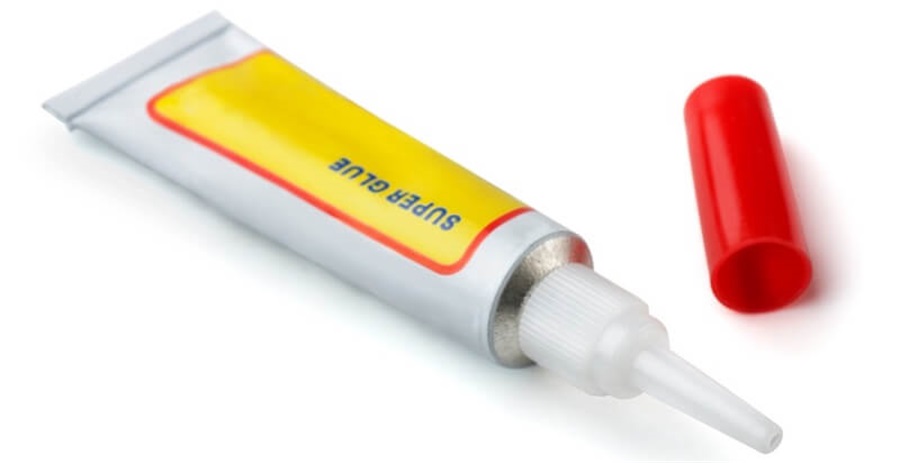

Super Glueg
Super glue dries super fast in five minutes in an ambient temperature of 25°C.
The higher the temperature, the quicker the drying time.
It can be used to bond plastic to plastic, plastic to metal, metal to metal, and once adhered, only a knife tool or heat can separate them.
The binding strength between plastic and plastic is the most effective, and very close to the binding power of ABS, which is used extensively for handmade manufacturing improvements.
C3.3.3 Mouse tail pipette (Glue pipette)
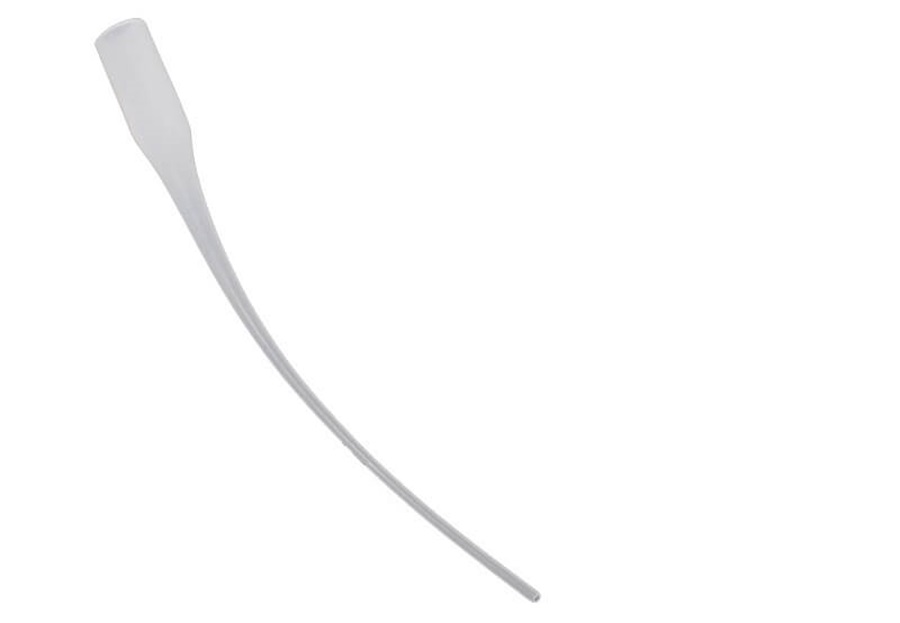

Mousetail pipette (Glue pipette)
This can be fixed to the top of UHU glue or super glue to effectively control the flow and quantity of glue dispensed on the material, which raises the efficiency of the architectural model making process.
The thin and long slender pipe of the mouse tail pipette can be cut according to needs.
C3.3.4: Hot glue gun
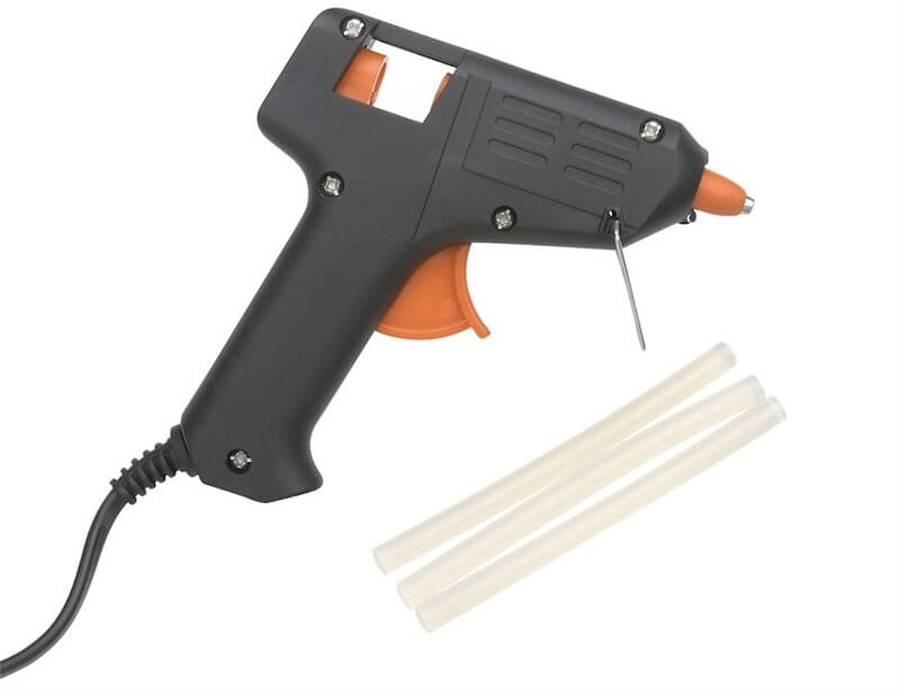

Hot glue gun
Hot glue has the fastest drying speed with a strong adhesive property.
It is used on material that is non-porous, such as metal.
During the building of a 3d sclae model, we like to use hot glue to hold the trees and cars onto the landscape, as it is easy to use and fast-acting.
Hot glue is slightly less neat, hence will not be suited for use on a piece of highly polished work.
Also, take care when using hot glue to prevent burn injuries.
Lastly, the durability of the glue gun is short. It does break easily, and will require replacement.
C3.3.5: Double-sided tape
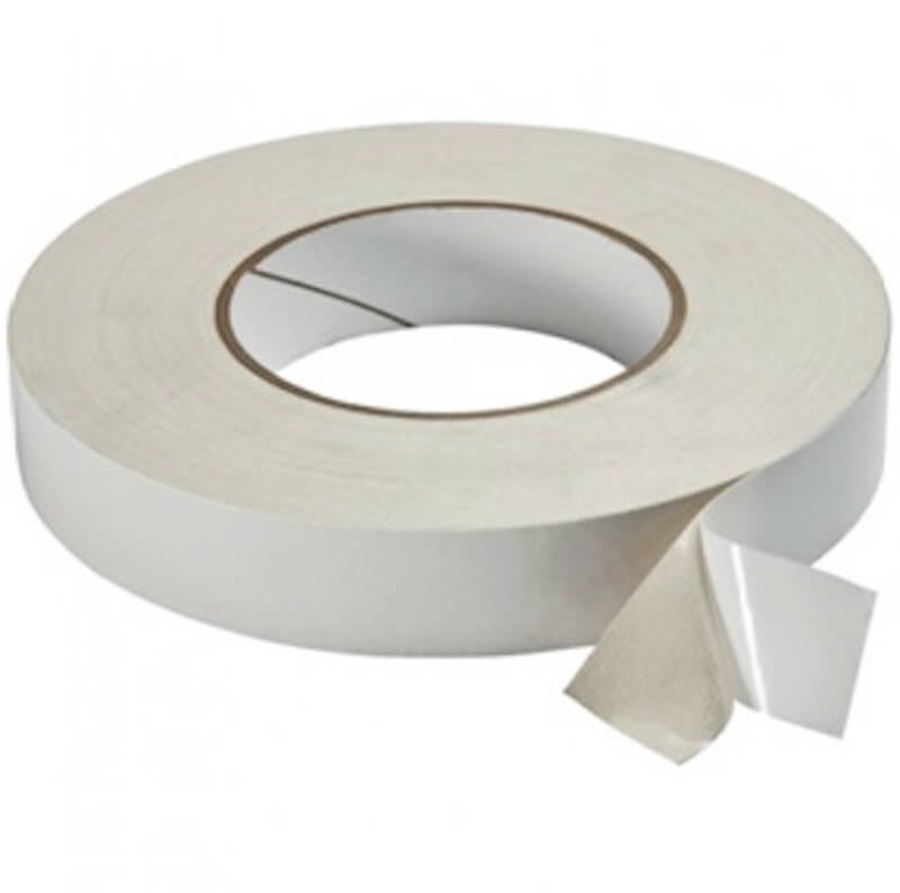

Double-sided tape
Double-sided tape works either as a temporary or permanent fixation in architectural model making.
It is a strong, neat, and can be adjusted accordingly, but be sure of the point where you want the tape to be before sticking it down as it cannot be removed without damaging the paper or foam underneath.
C3.3.6 Adhesive tape

Adhesive tape
Deciding when to use double-sided tape or glue is all down to the habit of an individual.
The bonding strength of an average double-sided tape used in the construction of the architectural model is slightly weaker than glue.
However, it is practical and convenient when there is a need for a temporary fix or if the material is transparent and easily dirtied, or has a wide surface area.
C3.4: Tweezers

Tweezers
Small tweezers come in very handy when picking up very tiny components.
The tweezers come straight, with an angle or a flat ending, which can pick up delicate objects conveniently.
These three different types of tweezers are used in architectural model making, and it is a must to possess a set.
Tweezers are easy to find, but cheaper ones tend to made from weak, inferior materials, so they will bend easily, making it hard to use resulting in lower productivity.
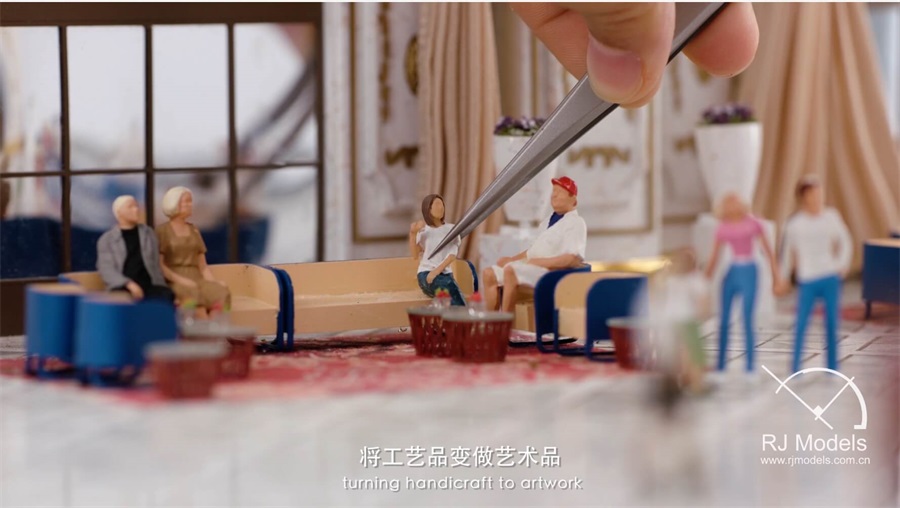

We can use tweezers to pick up delicate objects conveniently
Though slightly more expensive, we highly recommend purchasing tweezers specifically for architectural model making or high precision tweezers, as the pointed end will align when shut, the handle is stronger, and the pointed end clasps together with a bit of flex.
It is much more comfortable to use during the model making.
C3.5: Sandpaper

Sandpaper
When carving and shaping wood to build a 3d scale model, constructing a topography using polyethylene foam, or creating an irregular structure, other than cutting to form, there is also a need to polish.
Both processes require the use of a sanding tool like sandpaper. It has fine grit of metal powder or millstone glued to one side.
It is easy to use and can be cut into different sizes. Sandpapers in the market are categorized into numbers known as the grit size.
The larger the number, the finer the abrasive particles and this very fine grit is used to give an art piece its finishing polish.
There are different varieties of sandpaper to suit different uses.
You can wrap the sandpaper around a wooden block or acrylic board for use or you can buy a dedicated sanding block.
Plexiglas can be cut using a table saw, or band saw, and the edges can be polished and shaped using a belt sander.
It is a must to examine the shape frequently during the sanding process.
I check on the shape of the object being sand at regular interval during the sanding process to avoid over-sanding.
C3.7 Dusting Brush

Dusting Brush
This is used for dusting, especially for particles produced from the sanding or polishing process.
Dust can also accumulate on an architectural model after a while, but we can restore the texture and look of a model by gently dusting away all the accumulated dust.
The brush bristle must be soft to prevent damage to the 3d scale model.
C3.8: Cutting Mat
Cutting Mat
Cutting mats come in different measurements and colors.
It is best to have a cutting mat similar in size to your worktop and a smaller spare one that can be moved around.
Some people replace a cutting mat with cardboard.
However, as the cutter is very sharp, it will cut through the cardboard and, with time, the cutter may slip along previous cuts on the cardboard and reduce the precision of each knife stroke.
Hence it is better to use a cutting mat.
A cutting mat also does not blunt the knife and will prevent damage to the worktop.
Conclusion
Whichever techniques you choose to use in an architectural model making project depends on the circumstances and the level of your model making skills.
Search for material that can be used and push the use of that material to its limit. This requires sharp thinking, and innovation to achieve the perfect result.
CHAPTER 4:
3D Printing for Architectural Model Making
C3.1 What is 3D Printing
3D printing for architectural model making can show the architect’s design concept before it is built.
It presents better understanding and clarity for architects and developers and can discover the potential of certain issues that may occur in the project well in advance.
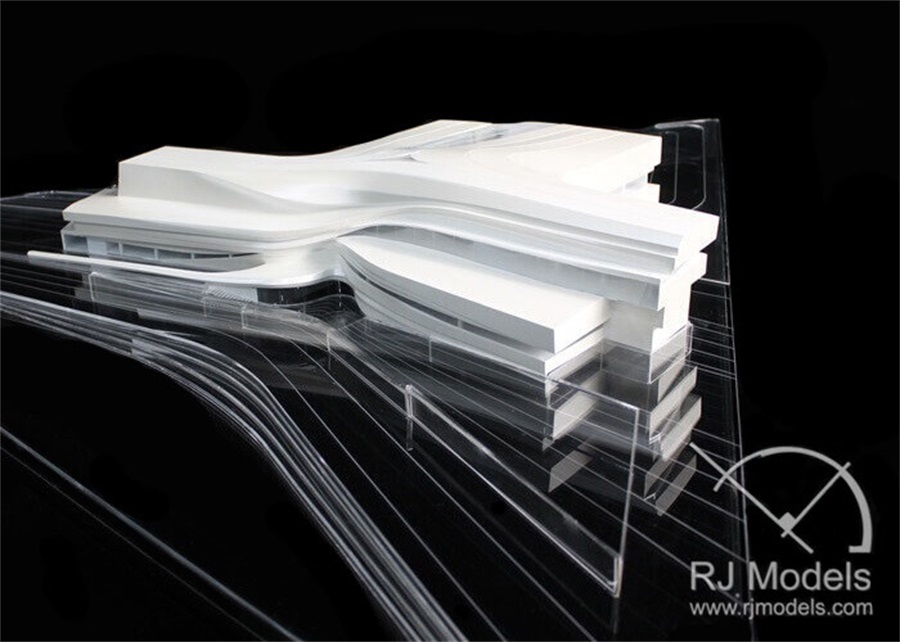
Complex and intricate architectural model making components, such as façade with multiple curvatures, folds, perforations, or structure with twisted and weaving elements, can now be produced easily and efficiently with 3D printing.
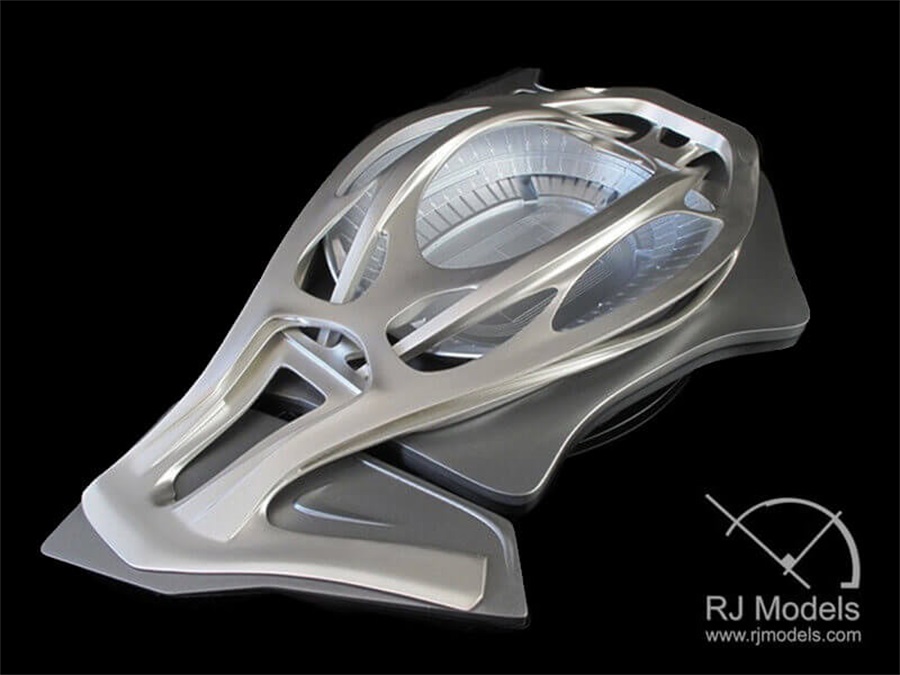

3D Printed Model which is designed by Zaha Hadid Architecture
This allows geometries created by designers can be realized in a physical model to be presented to their client.
We see an increase in 3D printing model, especially with the new generation of designers who have very quickly embraced this technology thanks to its lower cost, faster turnaround time and quality assurance.
3D printing in some cases can reduce the cost of production as a result of shorter production time.
Traditionally, architectural model makers create components from material(s) to realize designers’ intent, whilst 3D printing can complete this task from the digital file to the finished object, eliminating wastage of material and saving the manpower cost
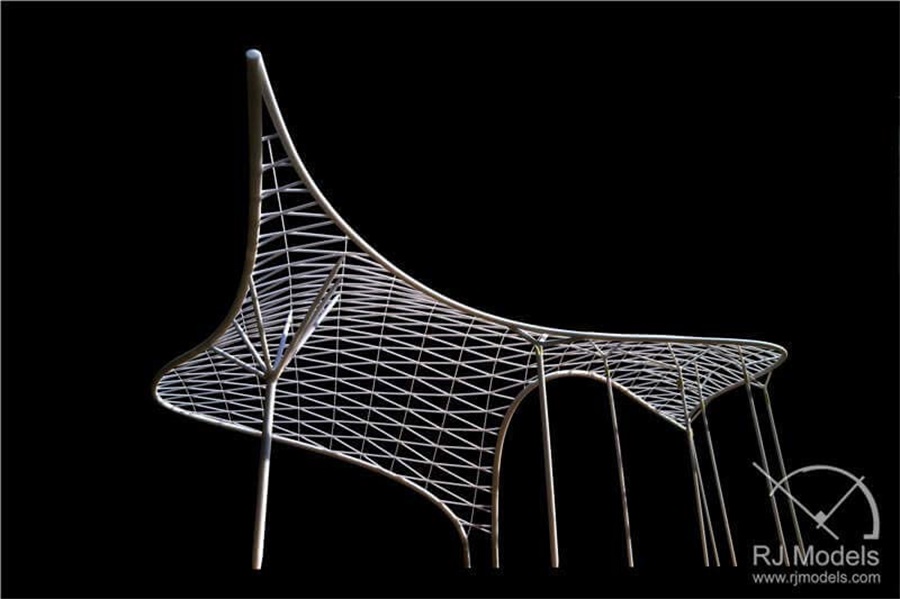

3D Printed Frame Model
Labor cost in the architectural modal making industry is consistently increasing.
3D printing can free up manpower and greatly reduce production costs.
3D printing technology can improve productivity.
Shorter architectural model making time allows designers more time to fine-tune their designs.
In comparison to the traditional way of model making, approximately 30% to 70% of time and cost savings can be achieved.
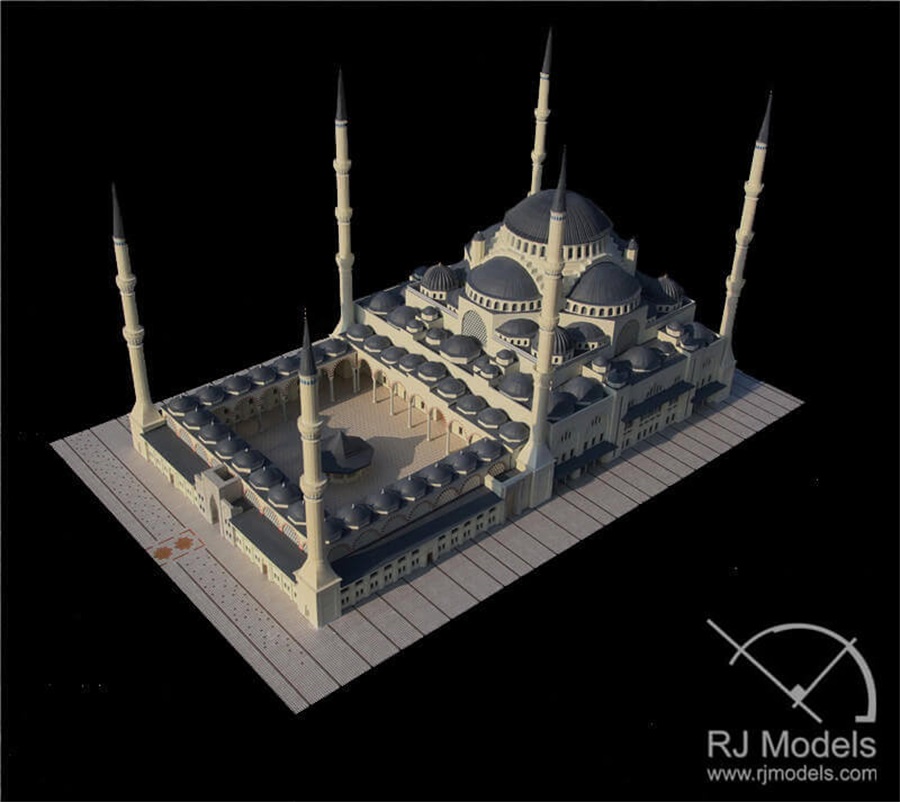

3D Printed Mosque Model
C 3.1 3D Printed Architectural Models by RJ Models
RJ Models has been in the model making business for more than 20 years and has been using 3D printing as soon as the technology was made accessible to the general public.
RJ Model has been producing 3D printing models for world-renowned architects such as Foster + Partners, Zaha Hadid Architect, KPF, SOM, OMA, etc.
Architectural Designers can send data to marketing@rjmodels.com.hk and we will provide a price proposal within 24 hours.
You can enjoy our professional 3D printed architectural model making services, delivery, installation, and maintenance.
RJ Models’ expertise can help designers save model making production time and costs.
C 3.2: The Price range of RJ Models 3D architectural models.
When 3D printing was first introduced, its cost was higher than the traditional manufacturing process.
As the technology is now very mature, components can now be produced with minimal error, the end product is much more durable, and finishing is much desirable.
This, as a result, offers very good value for money.
RJ Models charges approximately USD500 for a 3D printed model that measures 200mm x 100mm x 100mm.
3D Printed Architectural Model
This cost includes post-printing processes such as sanding, spray painting by professional model makers and worldwide delivery by a reputable courier company.
C3.3: Requirement of building design software programs for 3D Printed Architectural Model
RJ Models is also proficient at using the following software:
Sketchup,
Rhino,
3D Max,
3D AutoCAD,
Proe ,
Solidworks,
Ug,
Magics, etc.
If you preferred software programs are not listed above, RJ Models can always find a way to turn your designs into a model.